Translate
domingo, 20 de mayo de 2018
Curso para Data science
Edx me mando un mail sobre cursos para Data science y yo como soy tan bueno, decidí compartirlo:
jueves, 17 de mayo de 2018
Apache Avro
Apache Avro es un sistema de serialización de datos.
Avro proporciona:
- Estructuras de datos ricas
- Un formato de datos binario compacto, rápido.
- Un archivo contenedor, para almacenar datos persistentes.
- Llamada a procedimiento remoto (RPC).
- Integración simple con lenguajes dinámicos. No se requiere la generación de código para leer o escribir archivos de datos ni para usar o implementar protocolos RPC.
Cuando los datos de Avro se almacenan en un archivo, su esquema se almacena con él, de modo que los archivos pueden ser procesados posteriormente por cualquier programa. Si el programa que lee los datos espera un esquema diferente, esto se puede resolver fácilmente, ya que ambos esquemas están presentes.
Cuando se usa Avro en RPC, el cliente y el servidor intercambian esquemas en el enlace de conexión. (Esto se puede optimizar para que, en la mayoría de las llamadas, no se transmitan realmente esquemas.) Dado que tanto el cliente como el servidor tienen el esquema completo del otro, la correspondencia entre los mismos campos con nombre, campos faltantes, campos adicionales, etc. puede resolverse fácilmente .
Los esquemas Avro se definen con JSON. Esto facilita la implementación en Lenguajes que ya tienen bibliotecas JSON. Avro proporciona una funcionalidad similar a sistemas como Thrift, Protocol Buffers, etc. Avro difiere de estos sistemas en los siguientes aspectos fundamentales.
- Tipado dinámico: Avro no requiere que se genere ese código. Los datos siempre van acompañados de un esquema que permite el procesamiento completo de esos datos sin generación de códigos, tipos de datos estáticos, etc. Esto facilita la construcción de sistemas e lenguajes genéricos de procesamiento de datos.
- Datos no etiquetados: dado que el esquema está presente cuando se leen los datos, es necesario codificar considerablemente menos información de tipo con los datos, lo que da como resultado un tamaño de serialización más pequeño.
No hay identificadores de campo asignados manualmente: cuando un esquema cambia, tanto el esquema antiguo como el nuevo siempre están presentes cuando se procesan los datos, por lo que las diferencias se pueden resolver simbólicamente, usando los nombres de los campos.
Dejo link: https://avro.apache.org/
Vue Mastery
Quiero compartir este mail sobre la pagina Vue Mastery dado que hay muchos recursos del framework Vue.js, y nada más ...
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
martes, 15 de mayo de 2018
Machine Learning Yearning
Como les conté en un post anterior. Andrew Ng esta sacando un libro sobre machine learning.
Me llego otro mail del amigo Andrew Ng sobre su nuevo libro:
Me llego otro mail del amigo Andrew Ng sobre su nuevo libro:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
domingo, 13 de mayo de 2018
Dstream
Dstream es la abstracción básica en Spark Streaming y representa una stream continuo de datos.
DStream se puede crear a partir de flujos de datos de entrada procedentes de fuentes como Kafka, Flume y Kinesis, o aplicando operaciones en otros DStream. Internamente, un DStream se representa como una secuencia de objetos RDD.
Similar a RDD el DStream soporta:
- map
- flatMap
- filter
- count
- reduce
- countByValue
- reduceByKey
- join
- updateStateByKey
jueves, 10 de mayo de 2018
Apache Spark Streaming
Con el procesamiento de datos en streaming podemos analizar los datos en tiempo real, lo cual es muy útil en muchas situaciones. Apache Spark provee una librería para procesar streaming, que como no era necesarío un nombre difícil o original lo bautizaron Apache Spark Streaming.
El procesamiento de streaming se utiliza para analizar información que viene de sensores, iot, busquedas, logs de paginas web, el trafico a servidores, etc. Ejemplos de su uso podrian ser: monitorización de servidores o del comportamiento de usuarios en paginas web, etc.
Spark Streaming es una extensión de Apache Spark API y como ya digimos Apache Spark Streaming hace facil la creación de procesos tolerante a fallos para procesar información en tiempo real.
Desde la versión 2.0, Spark streaming soporta una nueva librería de streaming llamada
Structured Streaming, el cual ofrece un procesamiento de streaming escalable y tolerante a fallos basado en Spark SQL. Podemos utilizar dataset and la Api de dataframe en Scala, Java, Python o R para escribir agregaciones de streamings. Structured Streaming provee un camino para el procesamiento sin que tengamos que razonar mucho sobre el procesamiento.
Spark Streaming funciona dividiendo la transmisión en pequeñas porciones de datos (llamados micro-batches) en un intervalo predefinido (N segundos) y luego convierte cada micro-batch en un RDD. Nosotros podemos procesar estos RDD con las operaciones : map , reduce , reduceByKey , join , y window. Los resultados de estas operaciones RDD se devuelven en lotes. Por lo general, almacenamos estos resultados en un almacén de datos para un análisis posterior, para generar informes, o para enviar alertas basadas en eventos.
Es importante configurar correctamente el intervalo de tiempo para Spark Streaming, en función del caso de uso y los requisitos de procesamiento de datos. Si el valor de N es demasiado bajo, entonces los micropaquetes no tendrán suficientes datos para dar resultados significativos durante el análisis.
Los datos de streaming pueden ser procesados desde diferentes fuentes :
- Kafka,
- Flume,
- Twitter,
- ZeroMQ,
- Amazon’s Kinesis, and
- TCP sockets
martes, 8 de mayo de 2018
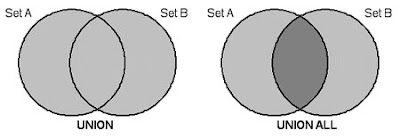
UNION vs UNION ALL
Principalmente el problema es que ambos tienen funcionalidades distintas. El UNION y el UNION ALL parecen funcionar igual pero tienen una pequeña diferencia. El UNION descarta los resultados en común entre los dos SELECT, en cambio, el UNION ALL no hace ningún tipo de verificación.
Por este motivo, el UNION ALL es más eficiente que el UNION.
Si sabemos que las 2 consultas a unir no van a tener repetidos es buena práctica usar el UNION ALL
LAG y LEAD en Oracle
Tenemos que relacionar un registro con su anterior o su posterior en una sola sentencia y devolver ese registro también.
Estas dos funciones “LAG y LEAD” lo permiten sin tener que realizar una self join.
LAG() devuelve el valor de la anterior fila y LEAD() el valor de la siguiente fila.
SELECT DNI,
LEAD(DNI) OVER (ORDER BY DNI) POSTERIOR,
LAG(DNI) OVER (ORDER BY DNI) ANTERIOR
FROM PRUEBA;
DNI POSTERIOR ANTERIOR
0001 0002
0002 0003 0001
0003 0004 0002
0004 0005 0003
0005 0006 0004
0006 0007 0005
Estas dos funciones “LAG y LEAD” lo permiten sin tener que realizar una self join.
LAG() devuelve el valor de la anterior fila y LEAD() el valor de la siguiente fila.
SELECT DNI,
LEAD(DNI) OVER (ORDER BY DNI) POSTERIOR,
LAG(DNI) OVER (ORDER BY DNI) ANTERIOR
FROM PRUEBA;
DNI POSTERIOR ANTERIOR
0001 0002
0002 0003 0001
0003 0004 0002
0004 0005 0003
0005 0006 0004
0006 0007 0005
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)